What are Voltage Fluctuations, and why do they matter?
Mains Voltage fluctuations are variations of the AC voltage on an incoming supply. Some of these mains supply voltage variations can be short-term in nature. However, in some cases where the incoming mains supply has severe problems, they can be a continual cause of concern.
These fluctuations are far more common than you probably imagine, and regularly cause
damage to connected sensitive electrical and electronic equipment. While historically, the average consumer may not have been too concerned about the stability and quality of their incoming power, many of the appliances they now use have changed in nature, becoming far more digitally based and, as a result, more voltage sensitive
Most consumers including, industrial, commercial, and domestic users worry about the effect these voltage fluctuations can have on their electrical equipment, whether it’s the equipment’s ability to perform critical day-to-day tasks efficiently and safely. Or to protect sensitive equipment from damage and the resulting costs, both directly and indirectly that can be caused by these ever-present vagaries in the utility mains supply
What are the causes of Voltage Fluctuations?
| 1. Poor Incoming Power Supply Quality | |
 | In today’s digital age, global network power grids have evolved towards more complex structures. The consumers’ demand for a more reliable, secure electrical supply has increased significantly. As a result, the need for a reliable quality power source is now more vital than ever before. Historically the problem has been widely held to be an issue of the less developed countries, but in recent years even in Europe and North America, with insufficient investment in new generation capacity and the failure to replace decommissioned fossil fuel and nuclear power stations, the existing supply networks have been struggling to keep up with the demand. As a result, brownouts (voltage drops below the usual mains supply level) are not uncommon, and in the worst cases, consumers are experiencing total power outages (blackouts). These grid-wide brownouts typically occur when the demand for power exceeds the generated supply capacity available. To prevent a complete blackout, energy suppliers can even decrease the network voltage by up to 10% to 25% for a short period of time until the peak demand subsides. |
| 2. Load Changes | |
 | Voltage fluctuations can occur due to sudden changes in demand caused by the switching of heavy electrical equipment and by starting large electric motors, both on-site and by other consumers on the same local supply network. These fluctuations are caused by the sudden drawing of a vast amount of current on the local distribution networks. |
| 3. Electrical Installation | |
 | Improper and poor wiring can also lead to voltage fluctuations and an irregular electricity supply. Poor wiring can result from corroded or loose connections on-site or in the power lines that feed the site. Increasing demands on the existing wiring can cause a significant local voltage drop if the sizing of the cables is insufficient to carry any increase in the designed load. Insects, pests and other animals can also inadvertently cause damage to the electrical installation. |
| 4. Natural Causes | |
 | Voltage fluctuations due to external natural causes are unpredictable and often very damaging, resulting in sudden and excessive voltage surges. Such events usually result from disruptions on the transmission power lines caused by direct and induced lightning strikes and damage to power lines by fallen trees caused by storms and heavy rainfall. In these events, sensitive electrical appliances such as computers, TVs, air conditioners etc., pay a heavy price. |
| 5. Interference | |
 | Electrical interference can be caused by spikes or noise-induced onto the mains supply. Spikes are random fast-moving, high-energy bursts caused by lightning strikes, load shedding, switching, and inductive motors. Noise is interference superimposed onto the mains supply, caused by switched-mode power supplies, inverters, RF broadcast transmissions, microwave radiation, electric motors. In the worst-case scenarios, the resulting interference can cause distortion in the supply resulting in an unstable voltage. |
What are the types of Voltage Fluctuations?
The most visually apparent result of voltage fluctuations is flickering or dimming lights. However, when you look deeper, the effects can be far larger and considerably more alarming in terms of financial costs and disruption to modern life.
Most electrical and electronic equipment is designed to operate correctly within their specification, provided the voltage supply is within ±10% of nominal. However, some sensitive devices require stable incoming voltage to perform accurately, such as computers, medical laboratories, telecommunications, and test equipment.
| 1. Sags | |
 | Sags are short duration decreases below 80 to 85% of rated RMS voltage in the mains supply, which generally last for over several cycles. These are caused by the switching of heavy equipment, and large electrical motors on the mains supply. They can cause Sensitive equipment to lock or hang resulting in data loss and system resets. |
| 2. Brownouts | |
 | Brownouts are long term sags in the mains supply voltage which can last up to hours or days. They are caused when the nominal steady-state RMS voltage falls by a relatively constant percentage. They can be caused by heavy equipment being turned on, the starting of large electrical motors, overloading of the supply network or just low voltage output from the generating source. Brownouts can cause equipment to malfunction or completely shut down. |
| 3. Over-Voltage & Surges | |
 | Over-Voltage & Surges are short duration increases above 110% of the rated voltage of the mains supply, usually for 1 or more cycles. These are caused by heavy equipment being turned off or high voltage output from the generating source. When surges occur equipment can suffer from premature failure. The high voltage causes wear and tear and general component degradation. This is often unnoticeable until failure occurs. Unusual heat output can be an early sign of problems ahead. |
| 4. High Voltage Spikes | |
 | High Voltage Spikes these are very fast high energy surges or spikes with a rapid rise in voltage up to 6,000 volts with a duration between a few microseconds up to ½ a cycle. Caused by the switching of electrical equipment, especially heavy inductive loads, arcing faults, or atmospheric electrical disturbance, such as lightning strikes and static discharges. Equipment can lock, hang, crash and even suffer permanent damage which inevitably causes data loss and corruption. |
| 5. Electrical Noise | |
 | Electrical Noise is a high-frequency noise either common or differential mode, superimposed onto the mains supply. Common-mode noise is interference between the live and neutral conductors and the earth, whilst differential mode noise is interference between the live and neutral conductors. Caused by RF broadcast transmissions, microwave radiation, electric motors, relays, motor control devices, inverters, and switched-mode power supplies. Electrical noise can cause processing errors, computer lock-up, burned circuit boards, degradation of electrical insulation and equipment damage. |
| 6. Blackout and Mains Failure | |
 | Blackout and Mains Failure is when the mains supply fails completely, total mains failure is known as a blackout. Caused by storm and lightning damage to distribution networks, generation failure, equipment failure as a result of overloading. Resulting in complete disruption of equipment operation. Even a break in the mains supply of only several milliseconds is sufficient to crash, lock or reset many of the components that make up a typical data processing system. |
What are the effects of Voltage Fluctuations?
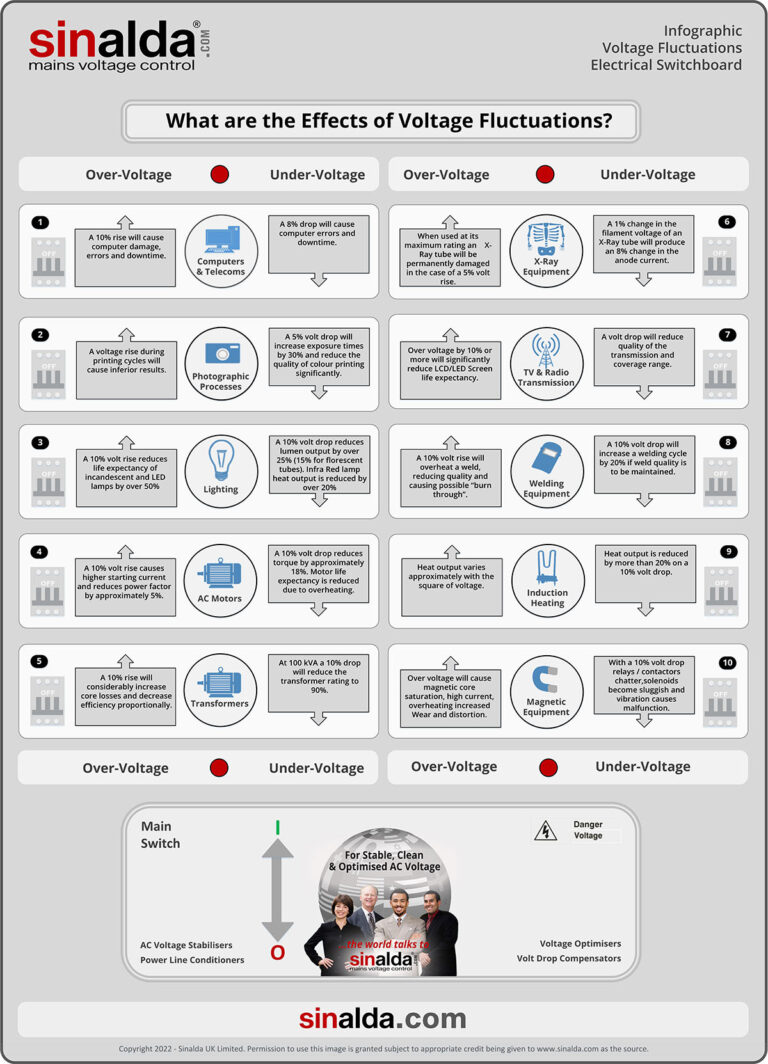
What is the cost of Voltage Fluctuations to Consumers?
Voltage fluctuations are common occurrences and can damage electrical and electronic equipment. These vagaries in the mains supply can significantly impact consumers’ productivity and noticeably reduce the operational life expectance of the equipment concerned. Whilst low / undervoltage can cause equipment to malfunction, high / overvoltage can cause serious damage, and make equipment operate inefficiently by consuming more power than required.
The financial cost to commercial and industrial users is considerable, especially for operations that depend on voltage-sensitive equipment. These costs typically include –
- Revenue loss due to stopped production
- Increase in material and labour overtime costs due to rework
- Damage to customer satisfaction due to late deliveries
- Unbudgeted equipment maintenance and replacement costs
- The rise of the expenses associated with breaches of environmental and safety issues
Some so-called ‘informed’ commentators reckon the actual costs could be as much as 8% of annual revenue!
What is the solution to Voltage Fluctuations?
At Sinalda UK, we strongly recommend as a first step, you diagnose the issues and try to determine the cause of your voltage fluctuations.
Secondly, we would encourage the implementation of good housekeeping rules/preventative measures, such as –
- Ensuring the electrical wiring on site is up to standard and meets all the local regulations.
- Check that the wiring of the electrical installation is correctly rated for any increase of load that may have occurred after when it was first installed.
- All electrical and electronic equipment is regularly maintained and serviced ensuring optimum and efficient performance.
Finally, for the remaining factors that you cannot directly control, install a Sinalda Voltage Stabiliser or Power Line Conditioner. This will ensure your sensitive electrical and electronic equipment always has a stable and clean voltage supply – free from the vagaries of the voltage fluctuations on the incoming mains utility supply.
To learn more about our Voltage Stabilizers, and associated Power Conditioners, please check out our product listings online at Sinalda.com