Last Updated: 09 November 2021

Copyright 2021 Sinalda. Permission to use this image is granted subject to appropriate credit being given to www.sinalda.com as the source.
Power Quality in Angola
Angola continues to recover from the damage caused by a 27-year-long civil war and experiences regular brownouts and power outages in its capital, Luanda, and across the country, with a greater incidence in the humid months due to the use of air conditioning.
Current electrification rates are estimated at 36% (43% in cities and less than 10% in rural areas). As a result, both businesses and residents rely heavily on diesel generators for power.
Power Sector in Angola
The country is Africa’s second-largest producer of proven natural gas reserves in sub-Saharan Africa and the third-largest economy on the continent. With the economy being heavily dependent on oil production and the associated exposure to the volatility of global oil prices and dollar exchange rates, moving the economy away from its reliance on oil production is a clear priority for the government.
Diversification of the economy cannot be implemented without a constant and stable grid network. As a result, the development of the power sector is critical to the future of the country.
Currently, it is estimated that the country has a generation capacity of 6,400 megawatts (Power Africa – Nov 2018) of which just less than 60% is derived from hydroelectric sources, with natural gas and other fossil fuels sources accounting for the rest. Although substantial investments in the power sector have been injected from governmental level, capacity still lags behind the country’s demand.
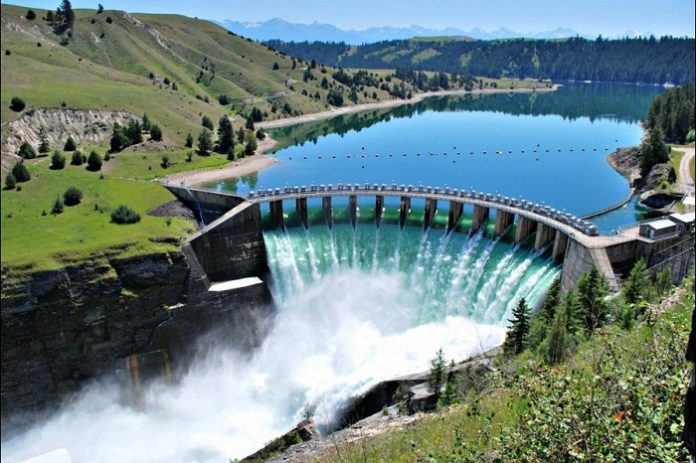

Laúca Hydropower Plant in Angola is the largest such facility in the Southern African country and among the biggest in the region, with an installed capacity of 2,070 megawatts.
Increasing electric power availability to diversify the economy and meet the increasing energy demand of a growing and more prosperous population, the Angolan government has stated that it wishes to increase generation capacity to 9,900 megawatts by 2025 and achieve a national electrification rate of 60%.
The energy consumption in Angola is mostly urban and residential. It is estimated that the residential sector demand accounts for 45% of total generation, followed by services (roughly 32%) and industry (approximately 9%).
Angola’s transmission infrastructure is one of the least efficient in Africa, being made up of three separate grid systems (northern, central, and southern), in addition to isolated grids in the east. The northern grid services Luanda, Bengo, Malange, Kwanza Norte, and Kwanza Sul. The central network includes Benguela and Huambo, and the southern grid covers Huila and Namibe. Plans exist to link the grids through a north-central-south backbone and expand the grid from 3,354 km to 16,350 km by 2025. Angola is currently a non-operating member of the Southern African Power Pool, but plans exist to connect to the pool through Namibia and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
To deliver on improving transmission and generation capacity, most commentators agree that external financing and private project development will be key, especially given the current government budget and economic downturn.
Angola holds great potential for renewable energy production. Mapping studies completed by the Ministry of Energy and Water in June 2014 identified potential for 17.3 GW solar power, 3.9 GW wind power, and 18 GW in hydropower throughout the country.
Although available generation capacity has grown significantly over the past years, transmission infrastructure has not been significantly enhanced. Moving forward, until these issues are addressed Angolans can continue to expect regular brownouts and power outages.
Share your Views and Experiences
Every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided above is accurate. No guarantees for the accuracy of the information is made.
So we are able to keep the content updated, and actual on the ground experiences can be shared with others, please feel free to contact us.