Last Updated: 01 November 2021
Copyright 2021 Sinalda. Permission to use this image is granted subject to appropriate credit being given to www.sinalda.com as the source.
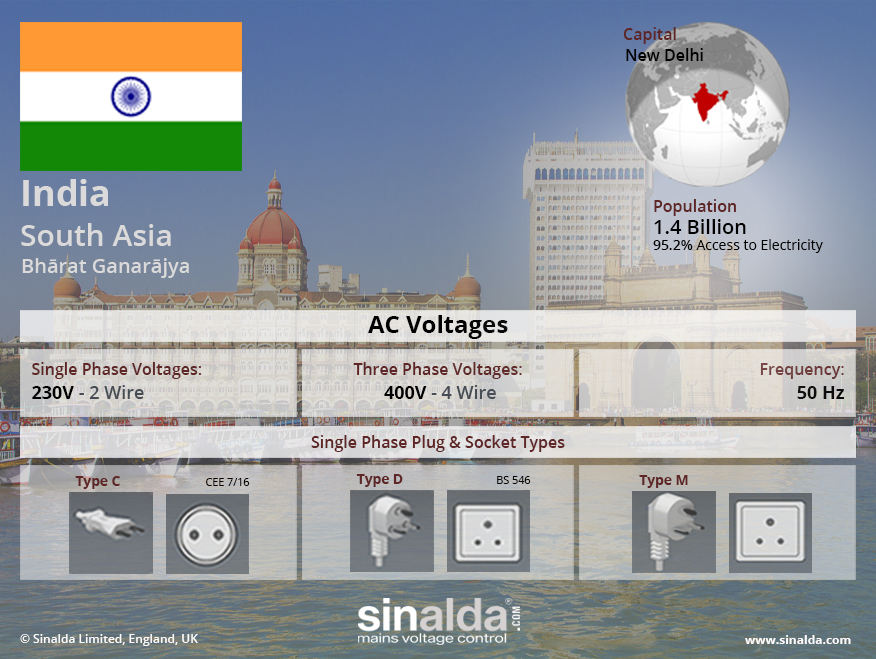
Power Quality in India
India is a rapidly growing country with a population of over 1.3 billion people. The demand for electricity has been growing exponentially, and India has been working hard to meet this growing demand. India’s electricity supply network is vast and complex, with a mix of state-owned and privately owned power generation and distribution companies.
India’s electricity supply network’s state varies depending on the region. The network is generally more reliable and efficient in urban areas than in rural areas. However, there are still many challenges facing the electricity supply network in India, including power outages, poor quality of power, and inadequate infrastructure.
Power Sector in India
Power outages are a significant issue in India, particularly in rural areas. A lack of investment in the electricity infrastructure, outdated equipment, and poor maintenance of existing infrastructure often cause these outages. The government has been investing in upgrading the infrastructure to improve reliability, but progress has been slow due to bureaucratic hurdles and funding constraints.
The quality of power in India is also a significant concern. Voltage fluctuations, low power factor, and poor frequency control can damage appliances and equipment. This is particularly problematic for industries and businesses that rely on a stable power supply to operate effectively. The government is addressing these issues by enforcing strict quality control standards and implementing new technologies, such as smart grids, to improve power efficiency.
Despite these challenges, the electricity supply network in India has made significant progress in recent years. The country has increased its installed power generation capacity from 135 GW in 2014 to over 380 GW in 2022. Renewable energy has been a major focus for the Indian government, with significant investments in wind and solar power. As a result, renewable energy now accounts for nearly 25% of India’s total installed power capacity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the state of the electricity supply network in India is improving, but there is still a long way to go. Power outages and poor power quality are significant issues that need to be addressed, particularly in rural areas. The government’s investment in upgrading the infrastructure and promoting renewable energy is a positive step, but it will take time to see the full benefits of these efforts.
Share your Views and Experiences
Every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided above is accurate. No guarantees for the accuracy of the information is made.
So we are able to keep the content updated, and actual on the ground experiences can be shared with others, please feel free to contact us.